Smart devices (IoT) co-exist and need to talk to each other within the network (here: smart home). Zigbee and Z-wave are two protocol standards upon which such smart devices work. These make use of the short range, low energy radio waves, instead of short-range Wi-Fi or Bluetooth. Both are identically different and differ in their functionality.
Zigbee and Z-wave have become global wireless standards of smart device communication. Both these are open-source, short-range wireless technologies and target almost similar applications for remote monitoring and control.
Both Zigbee and Z-wave have independent applications and both of these are suitable for Home-Area Networks (HAN) which are widely being used in the U.S.
Differences | Zigbee | Z-wave |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 2.4 to 2.483 GHz | 908.42 MHz |
| Modulation | 868 and 915 MHz bands (in Binary phase-shift keying (BPSK)) and offset quadrature phase-shift keying (O QPSK) | GFSK |
| Data Rate | 250kbits/s | 9.6/40 kbit/s |
| Range | 10 m | 30 m |
| Applications | Home automation, smart grid, remote control | Home automation, security |
| Network Topology | Mesh/Star/Tree | Mesh |
| Security | AES 128 bit symmetric encryption | AES 128 bit symmetric encryption |
| Which one is efficient? | Least or no interference at all. | It is less likely to face interference at this frequency as compared to its Zigbee counterpart. |
| Range | Physical range id approximately 10-20 metres. But its low consumption power limits to 10-100 metres line of sight depending upon power output and other environmental characteristics. | 100 m between the points of contact; works well within a home. |
| Device Support | Zigbee allows 65,000 devices or more | Z-wave supports 232 devices |
Zigbee was originally developed for commercial use, but now it is increasingly being used for industrial and residential purposes. It is low power, low cost, low complexity networking solution for Internet of Things (IoT).
It is based on IEEE’s 802.15.4 personal-area network (PAN) radio standard. The IEEE 802.15.4 standard provides layer 1 (Physical Layer) and layer 2 (Media Access Controller) of the network. The ZigBee stack software provides the network and applications layers.
It was started as an alternative source of Bluetooth and Wi-Fi device applications. Zigbee Alliance since then maintains the IEEE 802.15.4 standard.
Zigbee based applications can either function on mesh topology, or tree topology or even on star topology depending upon the requirements.
Obviously, all the branch nodes are connected with a master coordinator or the central node. If in case any of the two nodes are not able to communicate, they can communicate both-ways via links within range acting as repeaters. Zigbee based applications can support up to 65k nodes.
Image Source: https://dgit.com
ZigBee was developed to be flexible and scalable. It supports nearly 2500 brands as compared to Z-wave that supports just 2400 brands. It helps in designing specific application software known as profiles. These in return connect with ZigBee stack and make it faster and easier for manufacturers to create wireless products for specific applications. Provided these are available include home automation, smart energy, telecommunications, healthcare and remote control (Rf4CE or Radio Frequency for consumer electronics), retail services and building automation.
| Standard | IEEE 802.15.4 |
|---|---|
| Frequency | 2.4 GHz (for home automation), 784 MHz, 868 MHz, 915 MHz (country specific) |
| Range | 10-100 metres (line-of-speed) |
| Data Range | 20 Kbps to 250 Kbps |
| Network Type | MESH and Device-to-device |
Zigbee Specifications
Smart home, security monitoring, automatic doors and windows enabled with motion sensors, smoke sensor, water and gas leak sensors, smart lighting solutions with smartphone controlling applications, connected lighting with energy saving options, smart switches which doesn’t requires battery power source (receives power from energy harvesting), healthcare devices and applications, smart energy management applications like solar energy systems, hybrid vehicle charging, programmable communicating thermostats, neighborhood Area Networks (NAN) for utility operations which connects devices outside home, smart retail applications like locations tracking and electronics shopping tags, food safety monitoring, enhanced wireless devices to improve shopping experience
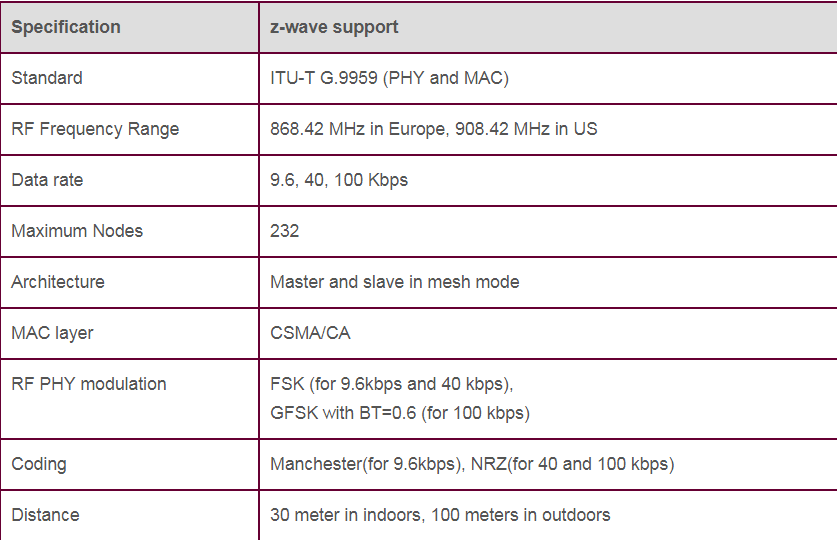
Z-wave was developed as a proprietary wireless standard by Zensys in 2008, before being acquired by Sigma Designs. Although Z-wave is not open like most other wireless standards it is available to most of the Zensys/Sigma Design customers. PHY and MAC layers of International Telecommunications Union (ITU) were included as an option in its new G.9959 standard.
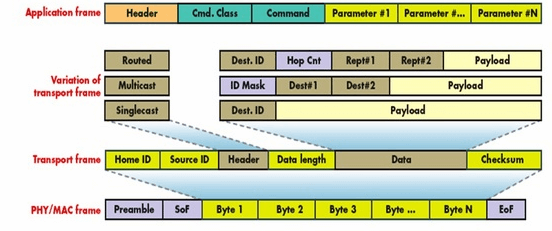
Protocol Architecture of Z-Wave
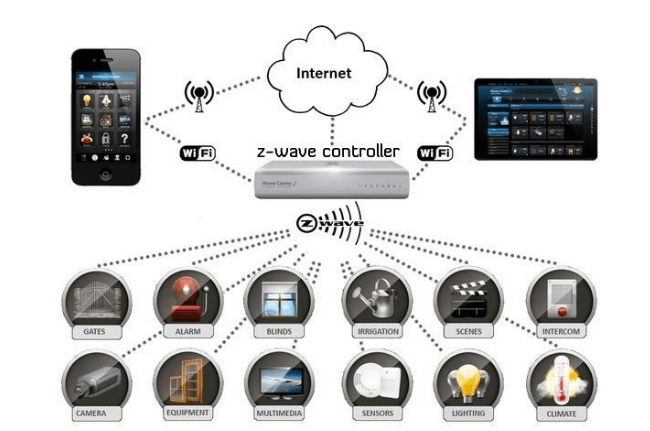
Image source: https://dgit.com
Z-Wave wireless mesh technology allows various nodes to interact. If two nodes are not within the range, they can link with other common nodes that are accessible to both previous nodes and exchange information. A Z-wave network can have a maximum of 232 nodes. Z-Wave monitors and controls various functions at home and small commercial offices.
It can manage lights, security, climate, smoke, locks, various appliances, remote controls etc. It can efficiently be used in smart electric meters to provide consumption data for home HVAC monitors and controls.
Smart Hub, Smart Lighting, Smart Locks, Smart Sensors, Smart Home Automation, Security and Alarm, Voice Controlled Application, Water Management, Smart Energy Management, Smart USB etc.
These two technologies although implementing Android app interactions with smart home devices, Bluetooth sensors or Wi-Fi network are still used in conjunction to send data to gadgets.
The applications that Zigbee and Z-wave target are almost the same. Zigbee is however considered more versatile, as it supports more brands as compared to Z-wave. It is as well configured for virtually any short-range wireless task. Profiles are easily available to Zigbee to minimize development time for common applications. Zigbee protocol is, however, difficult to configure and use as compared to Z-wave which is faster and simpler. Z-wave chips are available from Sigma Designs, while Zigbee chips are available from Ember, Freescale, Microchip Technology, and Texas Instruments.
Smart Home Solutions powered by Zigbee work as follows:
As soon as the user changes settings on a smart device, a signal is transmitted to the closest router. This signal is transmitted from the router to the server. The server sends this signal to the microcontroller – which processes all the data and sends the signal back to the sensors.
Zigbee includes a full range of protocols to create a fully-functioning network of sensors and smart home devices. Mobile App Developers have tapped into various opportunities provided by Zigbee technology by creating a smooth android app.
The smart home ecosystem will grow if the smart devices get access to open smart home API’s. Alexa Smart Home Skill API is one such example by Amazon, which allows third-party smart appliances by various manufacturers to communicate with Alexa. This API works to open up doors, switch on AC, turn-on or off lights, and manages motion sensors.
Making use of solutions like Bluetooth (commonly used in Fitness trackers) can sometimes be expensive or even non-supportive with some devices
All the devices within a smart home are controlled by microcontrollers. As it gets dark or cold, a light or temperature sensor can send signals to micro-controllers to turn on light and switch on the thermostat.
Trust team of android app developers at Konstant for every Home automation needs; allow you to measure your success against set goals and provide a clearer and specific idea of where your strategy may need adjustments. We will be happy to help!



Neeti Kotia is a technology journalist who seeks to analyze the advancements and developments in technology that affect our everyday lives. Her articles primarily focus upon the business, social, cultural, and entertainment side of the technology sector.
Or send us an email at: [email protected]